Table of Contents
A little story
Use of "to do"
Example: the future tenses
Table of Contents |
Questions and negations
A little story |
HOME |
back to
Use of "to do" |
go on to
Example: the future tenses |
translated by Class 8a of Clemens-Brentano-Realschule, Koblenz
A little story:
An old man lives in a crowded street
and everyday he must cross the street to go shopping. He isn't so good
at walking. That's why he needs some help for walking. The old man
whose name is Mr Verb has got a stick. He has given his stick a name. His
name is "Auxiliary".
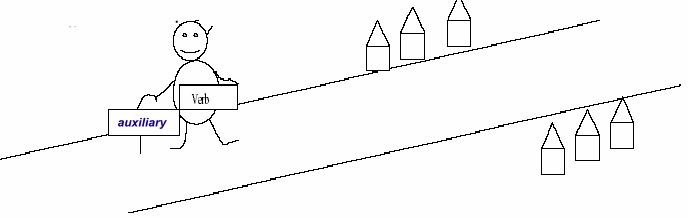
Auxiliary verbs are: can, must, be, would,
might, could, may, have�
Or simpler:
As soon as there follows another verb
the first one will be the Auxiliary. When Mr. Verb has got his stick with
him, he can get to the opposite side
 |
As you can see, the Auxiliary and the subject change their places. If there is a question with an Auxiliary this one will take the first and the subject the second place. |
But Mr. Verb is infirm/weak. So he sometimes forgets his stick.
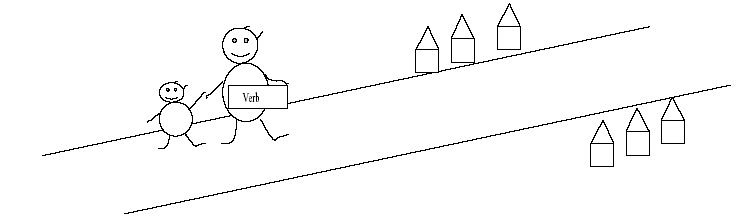
 |
There, where actually the auxiliary ought to be, there is a an empty space. Well, you can't put anything in front of the subject because there isn't anything available. But in a question there must be something in front of the subject. |
Therefore "do" jumps in. Little "do" is a very helpful boy. When Mr. Verb has done the shopping, he takes the shopping bag and carries it.
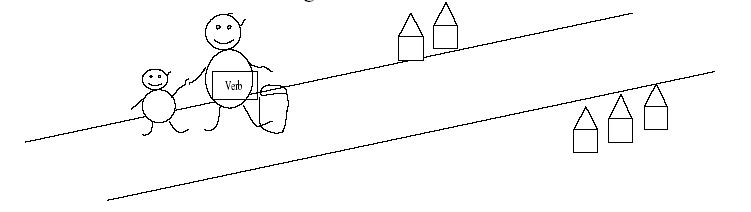
 |
When "do" takes the shopping bag he will become "does". And remember there is only one shopping bag. The verb hasn't got it anymore. He loses all his qualities |
The same thing happens in the simple past.
Here "do" will become "did".
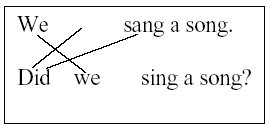 |
 |
So far as to the simple questions. This
transcription with "do" occurs only in simple present and simple past.
Because all other tenses are compound tenses and have an Auxiliary of their
own.
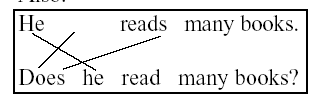
And at last here's the sentence diagram
of the English question once more:
|
|
So, the same principle is used in the
negation. Whenever we have an Auxiliary we simply put a "not" after the
Auxiliary. If the Auxiliary is missing we'll put a form of "to do" in front
of the full verb and let "not" follow.
Examples;
| I can play the piano. | I cannot (can't) play the piano. |
| We play cards. | We do not (don't) play cards. |
| He plays tennis. | He does not (doesn't) play tennis. |
| They went swimming. | They did not (didn't) go swimming. |
"Do" gets all the characteristics of the
verb again and the verb is in infinitive form.
|
Never combine "do" and "be" |
That means: If there is a form of "to be" in the sentence, there won't be a form of "to do", even if "to be" is the only verb in the sentence.
So, if everything is clear, you can challenge your knowledge in the following exercise. First you have to put the sentences in the negative form and afterward you'll have to find questions.

Table of Contents |
Questions and negations
A little story |
HOME |
back to
Use of "to do" |
go on to
Example: the future tenses |